8.1. Prevent Unwanted ConnectionsMost Fedora systems are connected to a TCP/IP network. You can guard against unwanted inbound connections to your system by using the built-in firewall. 8.1.1. How Do I Do That?To adjust the Fedora firewall graphically, select the menu option System Figure 8-1. Firewall configuration tool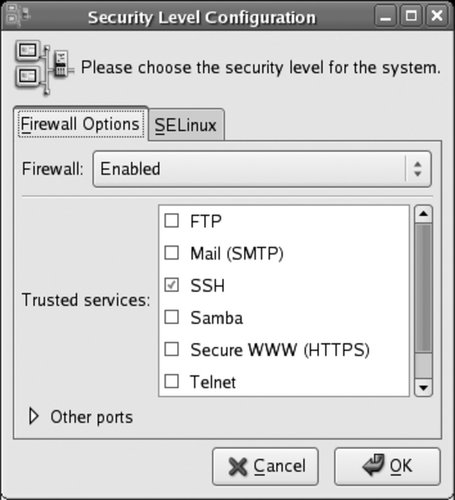
The control at the top of this window enables and disables the firewall. When the firewall is enabled, the lower portion of this window can be used to permit connections to your system for selected services; simply select the checkboxes for the desired services. SSH should remain selected to permit secure remote administration. To permit connections to services that are not listed, click on the triangle for "Other ports." The display will change to reveal an additional section, as shown in Figure 8-2. Figure 8-2. Configuring other ports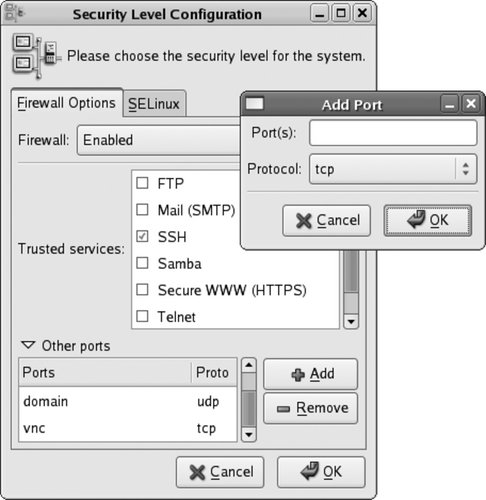
To add additional ports, click the Add button, and the window shown on the right side of Figure 8-2 will pop up. Enter the port number or the service name, select TCP or UDP for the protocol, and click OK.
When the firewall is configured to your liking, click OK. 8.1.1.1. Configuring the firewall in text mode# lokkit
The screen displayed in Figure 8-3 will appear. Use the Tab key to navigate among fields, the spacebar to select and deselect checkboxes, and Enter or the spacebar to activate buttons. Figure 8-3. Lokkit firewall configuration screen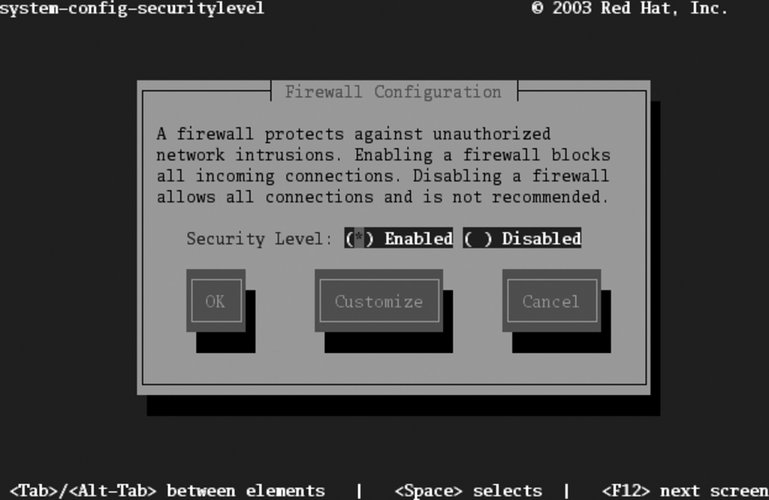
Enable or disable the firewall using the checkboxes. To customize the types of connections that are permitted through the firewall, tab to the Customize button and press Enter. The customization screen shown in Figure 8-4 will appear. Figure 8-4. Lokkit firewall customization screen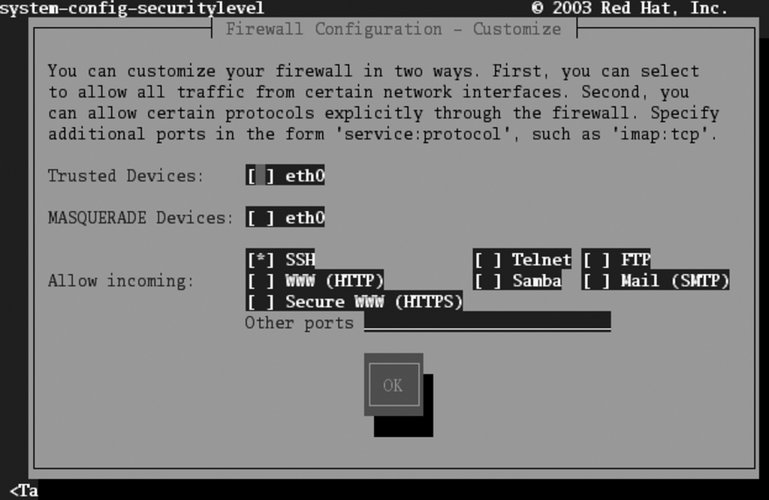
The Trusted Devices and MASQUERADE Devices checkboxes are applicable only to systems with multiple network connections. Do not select either of those options on a system with a single network interface.
Use the Allow Incoming checkboxes to select the services that will be permitted to connect to your system through the firewall. In almost all cases, SSH should be selected to permit secure remote connections for system administration. To allow incoming connections to services that are not listed, enter the port number or service, followed by a colon (:), and the protocol (TCP or UDP) into the "Other ports" field at the bottom of the screen. You will need to separate multiple entries with a space or comma. For example, to permit incoming connections to the VNC service as well as to a custom UDP service running on port 64447, use: vnc:tcp 64447:udp Select OK to return to the main screen (Figure 8-3); select OK on that screen to save your settings and exit. 8.1.1.2. Temporarily disabling the firewall from the command lineTo disable the firewall until the next reboot, stop the iptables service: # service iptables stop
To reset your firewall to the configured settings, restart the iptables service: # service iptables restart
8.1.2. How Does It Work?The Fedora firewall uses the kernel's iptables capability, which can filter packets based on their source, destination, port, protocol, contents, and current connection state. To view the current iptables configuration, use the -L option: # iptables -L Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination RH-Firewall-1-INPUT all -- anywhere anywhere Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination RH-Firewall-1-INPUT all -- anywhere anywhere Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination Chain RH-Firewall-1-INPUT (2 references) target prot opt source destination ACCEPT all -- anywhere anywhere ACCEPT icmp -- anywhere anywhere icmp any ACCEPT ipv6-crypt-- anywhere anywhere ACCEPT ipv6-auth-- anywhere anywhere ACCEPT udp -- anywhere 224.0.0.251 udp dpt:mdns ACCEPT udp -- anywhere anywhere udp dpt:ipp ACCEPT tcp -- anywhere anywhere tcp dpt:ipp ACCEPT all -- anywhere anywhere state RELATED,ESTABLISHED ACCEPT tcp -- anywhere anywhere state NEW tcp dpt:ssh REJECT all -- anywhere anywhere reject-with icmp-host-prohibited There are four chains of rules defined here:
Since the policy for each chain is ACCEPT, flushing (clearing) the rules will result in all packets being accepted. This is exactly what the iptables -F command does, which is executed when the iptables service is stopped. The graphical firewall configuration tool is system-config-securitylevel (which, in recent versions, also handles SELinux configuration). The character-based version is system-config-securitylevel-tui, which is also known as lokkit. Both of these tools save the firewall configuration in /etc/sysconfig/system-config-securitylevel and, from that configuration, derive a set of iptables rules that are saved in /etc/sysconfig/iptables. That file, in turn, is used by the iptables service (/etc/init.d/iptables) to configure the firewall; options that control the operation of the iptables service are stored in /etc/sysconfig/iptables-config. iptables is actually an unusual service. Most other servicessuch as cups, httpd, or gpmhave a server process that begins running when the service is started and that is stopped when the service is stopped; iptables, on the other hand, just configures the iptables facility in the kernel when the service is started or stopped, so there's no actual process running when the firewall is active. 8.1.3. What About...8.1.3.1. ...more complex firewall rules?The firewall interface provided by Fedora's system-config-securitylevel supports only the filtering of inbound (and forwarded) packets and is quite simple. However, the iptables mechanism supports much more complex filtering. Fedora Extras provides several alternate tools for firewall configuration, including firestarter, fwbuilder, and shorewall. 8.1.4. Where Can I Learn More?
|