Working with a Table

A database is made up of groups of fields organized into tables. A field is a specific category of information, such as a name or a product. Related fields are grouped in tables. You usually enter data into fields one entity at a time (one customer at a time, one product at a time, and so on). Access stores all the data for a single entity in a record. You can view a table in Datasheet or Design view. Design view allows you to work with your table's fields. Datasheet view shows a grid of fields and records. The fields appear as columns and the records as rows. The first field in a table is often an AutoNumber field, which Access uses to assign a unique number to each record. You can't select or change this value.
Enter a New Record and Move Around in a Table
 | In the Database window, click Tables on the Objects bar, and then double-click the table. |
 | Click the New Record button. |
 | Press Tab to accept the AutoNumber entry. |
 | Enter the data. If you make a typing mistake, press Backspace. |
 | Press Tab to move to the next field or Shift+Tab to move to the previous field. |
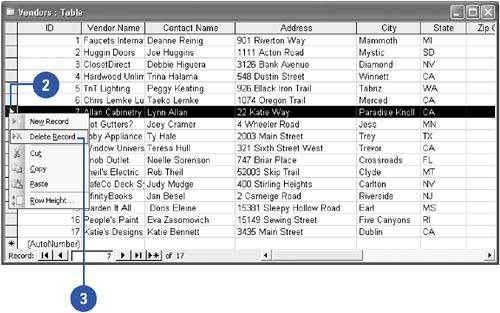
Delete a Record from a Table
 | In the Database window, click Tables on the Objects bar, and then double-click the table. |
 | Right-click the row selector. |
 | Click Delete Record. |
 | Click Yes. |
|