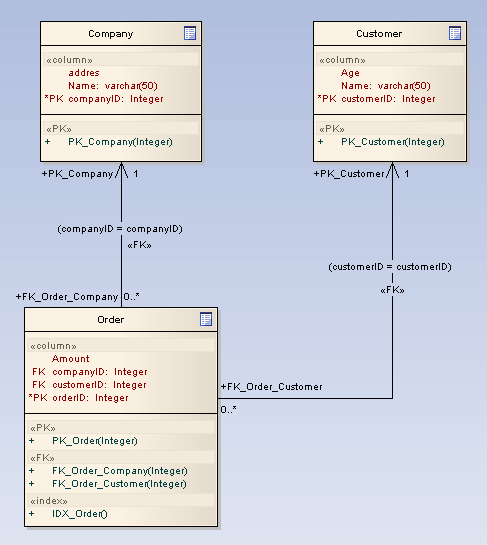
What is an Index?
An index is a sorted look-up for a table. When it is known in advance that a table must be sorted in a specific order, it is usually worth the small processing overhead to always maintain a sorted look-up list rather than sort the table every time it is required. In Enterprise Architect, an index is modeled as a stereotyped operation. On generating DDL, the necessary instructions for generating indexes are written to the DDL output.
What is a Trigger?
A trigger is an operation automatically executed as a result of the modification of data in the database, and usually ensures consistent behavior of the database. For example, a trigger might be used to define validations that must be performed every time a value is modified, or might perform deletions in a secondary table when a record in the primary table is deleted. In Enterprise Architect, a trigger is modeled as a stereotyped operation. Currently Enterprise Architect does not generate DDL for triggers, but nonetheless they aid in describing and specifying the table structure in detail.
What is a Check Constraint?
A Check Constraint enforces domain integrity by limiting the values that are accepted by a column.
Create an Index or Trigger
| 1. | Locate the required table either in a diagram or in the Project Browser window. |
| 2. | Use the context menu to open the Operations dialog. |
| 3. | Add an operation (with a name such as IDX_CustomerID or TRG_OnCustomerUpdate; the IDX_ and TRG_ prefixes are optional but help identify the operation). |
| 4. | Set the for the operation to or as appropriate (, and are also supported). |
| 5. | Click on the Behavior tab. |
| 6. | Enter the entire body of the trigger or procedure, or details of the check constraint, in the field. |
| 7. | Select the operation and click on the Columns tab. |
| 8. | Add the required columns in the required order then click on the button to save changes. |
Create a Check Constraint
| 1. | Locate the required table in either a diagram or the Project Browser window. |
| 2. | Use the context menu to open the Operations dialog. |
| 3. | Add an operation (such as CHK_ColumnName). |
| 4. | Set the for the constraint to and click on the button to save changes. |
| 5. | Select the constraint operation, then the Behavior tab. |
| 6. | Enter the entire check constraint clause (eg. ) in the field and click on the button to save changes. |
The example below shows how an index looks in a diagram: